Cloud adoption shows no sign of slowing in 2025. Firms of every size now run mission‑critical apps in the cloud, yet they still wrestle with three big worries: keeping data safe, scaling without drama, and paying only for what they use.
In 2024, Flexera found that managing cloud spend again outranked every other concern, with 27% of public‑cloud expenditure classified as waste.
These numbers explain why leaders now want a playbook that brings structure, savings, and safety, without slowing delivery. A steady, repeatable approach to day‑to‑day cloud work has moved from “nice to have” to “must have.”
This is where AWS comes into play, thanks to its Well-Architected Framework.
Why pick AWS for that job?
The numbers tell the story.
AWS revenue climbed roughly 20 percent year‑over‑year in 2023, reaching $28.8 billion in Q4 alone. You get more features, superior global coverage, and a deeper pool of managed services than any rival.
Yet a larger toolkit also raises the odds of misconfigurations, idle resources, and surprise bills.
Enter the AWS Well‑Architected Framework (WAF).
It comes across as a living rulebook that shows AWS cloud service providers how to achieve security, performance, resilience, cost, and sustainability right from the start. You also learn how to maintain them as workloads grow.
Up next, we’ll unpack the framework, the official toolset, and the concrete wins you can expect when the principles guide every design choice.
What is the AWS well‑architected framework?
The AWS Well-Architected Framework defines a set of guidelines and design principles. These exist to guide teams in building consistent, secure, dependable, and financially prudent systems on AWS.
Further down, this framework is based on the insights from numerous architecture reviews across many industries, ultimately distilling them into core categories called pillars.
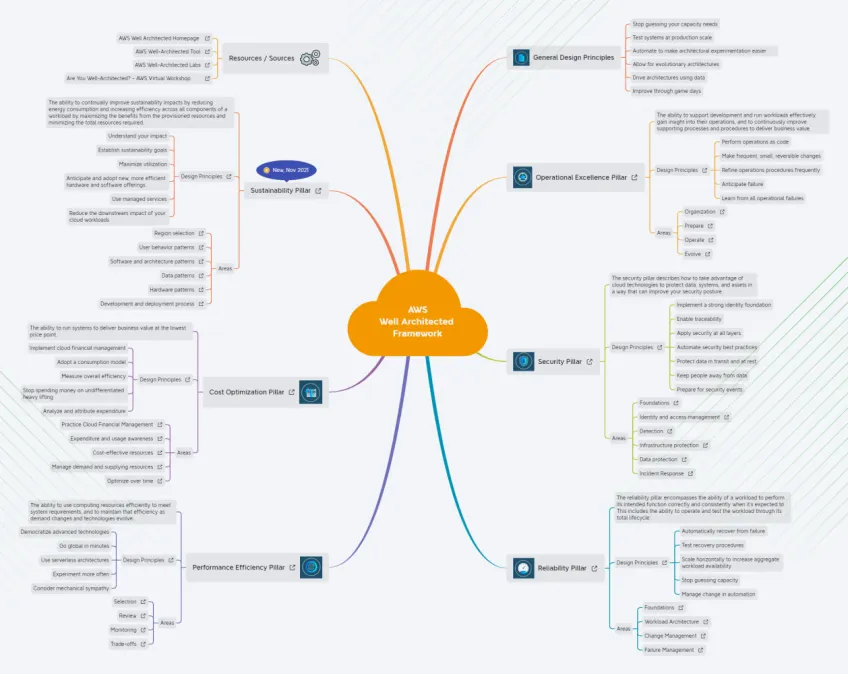
Pillars of AWS Well-Architected Framework
The AWS Well‑Architected Framework is a published collection of design principles. Based on thousands of real‑world cloud deployments, these framework pillars address core pain points of cloud adaptability.

Operational excellence
This pillar focuses on running and monitoring systems in a way that refines procedures through small, frequent changes. As you learn from every event, you should be able to manage workloads smoothly and update them without service breaks.
Security
Think of how you’ll protect data, manage identity, and test incident response. This pillar guards key information, systems, and identities through layered controls and continuous risk review.
Reliability
It is a pillar that prevents and recovers systems from failure with automation, backup, and multi‑site design. Your services will remain available and recover quickly when parts fail.
Performance efficiency
Select the right resource types and sizes; review often. This will allow you to match resource types and quantities to changing demand while avoiding slowdowns.
Cost optimization
Avoid unneeded spending, pick the best pricing model, and track the return on every dollar so that you only spend on resources that add business value and stop paying for the rest.
Sustainability
Reduce energy use and share responsibility for a lower carbon impact. Smart region choice and higher resource utilization will reduce the workload's environmental footprint.
What the framework includes?
AWS also backs the framework with practical resources. The Well-Architected Tool (WAT) in the AWS console scans your setup and flags risks tied to these pillars.
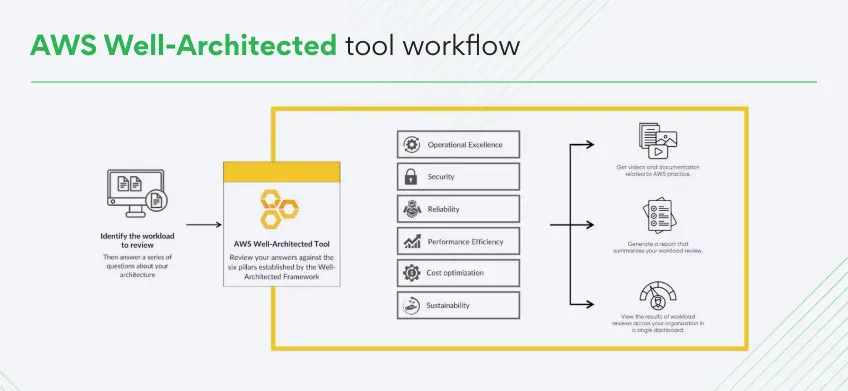
Here’s what the AWS Well-Architected Framework includes:
Well‑Architected Tool (WAT)
A free console wizard that scores any workload against pillar questions, highlights risk items, and tracks improvements over time.
Lens extensions
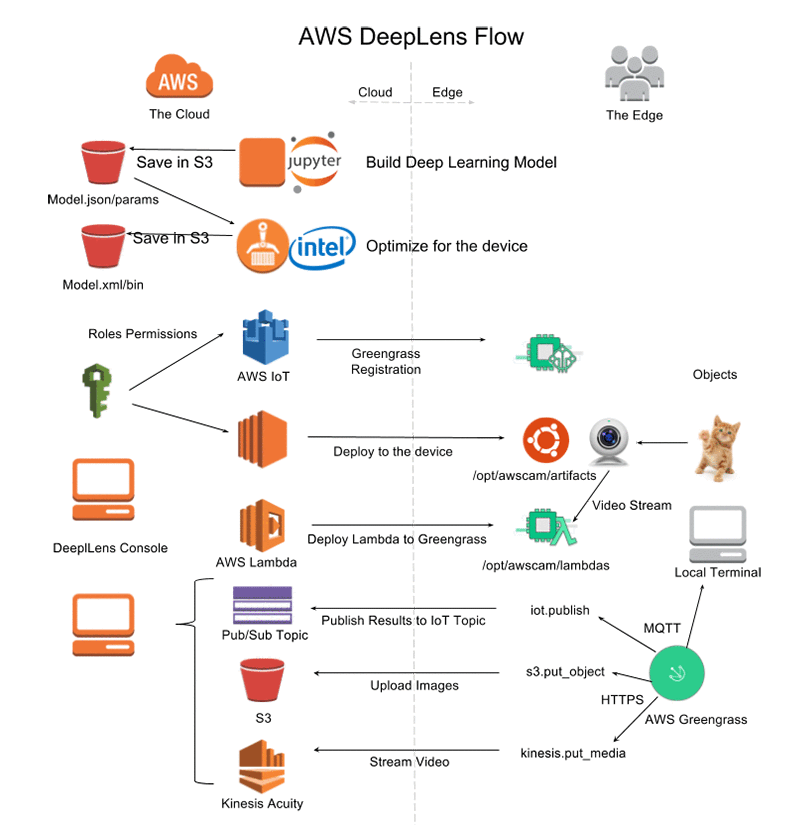
DeepLense Flow helps add specialized questions for areas like serverless or machine learning.
These extra question sets explore specialised domains such as Serverless, SaaS, IoT, Machine Learning, and Games.
Well‑Architected review
A structured workshop is often run with an AWS Partner. It captures the current state, grades each risk, and produces a 30/60/90‑day action plan.
Adopting these elements can help you pinpoint weak spots and set tangible goals, transforming the framework from a theoretical guide into a daily practice that elevates cloud success.
How does the framework shape modern cloud infrastructure?
Cloud services now span everything from virtual servers to fully managed databases, analytics platforms, machine learning pipelines, and beyond. Such a breadth carries huge opportunities for quick growth. But, they can also be confused unless there’s a way to measure and maintain quality.
A fintech startup spins up an account on Monday. By Friday, dozens of micro‑services run in three Regions, traffic doubles every other week, and a single mis‑tagged bucket can begin hiding a month’s worth of logs.
Stories like that fill every Slack channel in cloud engineering.
The AWS Well‑Architected Framework steps into this fast‑moving world, offering a checklist that keeps speed without letting risk creep in.
1. Matching tech goals to business goals
The AWS Well-Architected Framework pushes architects to translate abstract targets into numbers that matter to the firm.
The Framework translates board‑level aims like speed, margin, uptime, etc., into concrete engineering tasks. By tying every improvement back to one of the six pillars, your team can defend budget requests with clear, measurable outcomes.
Revenue teams want faster features, finance wants fewer surprises, and security wants proof of control. The six pillars give each camp common ground. For example, a product manager can point to the Performance pillar when asking for lower P95 latency.
2. Consistency and compliance
Under Performance, you’ll have to turn instance families, pick the right database engine, and add regional caches. The framework’s question set maps cleanly to regulations such as HIPAA and PCI DSS.
When a workload passes the Security pillar, auditors gain evidence for encryption, logging, and least‑privilege access without a separate discovery sprint.
That shortens audit cycles and keeps surprises off the board agenda.
Each decision rolls up to a measurable outcome: quicker pages, stronger defenses, smaller bills.
3. Risk mitigations
Common hazards like open S3 buckets, single‑AZ deployments, and missing backups are identified as “high‑risk issues” in the Well‑Architected Tool.
Because the tool tracks each fix, project managers can prove progress during quarterly reviews. Clear guidance sits right next to each flag, turning “fix it later” into “patch it today.”
4. Operational efficiencies
Templates born from Well‑Architected guidance feed straight into Infrastructure‑as‑Code files. Once the blueprints exist, new environments are prepared in minutes, resulting in fewer outages for on‑call engineers.
Over time, those scripts become a living library that reduces manual toil. Junior staff follow playbooks instead of tribal lore, and outages shrink from hours to minutes.
Read more: End-to-End AWS Consulting Guide: From Planning to Execution
Role of AWS Well-Architected Framework to boost cloud infrastructure
AWS hands builders a huge toolbox, yet the real game‑changer hides in the questions the Well‑Architected Framework asks.
The Well‑Architected Framework lays down proven engineering moves so teams can ship fast, sleep well, and spend only what they need.
Follow this Framework as a field manual. Each section tackles a different pressure point—uptime, spend, security, speed—and then provides concrete tactics. Walk through the manual and watch an ordinary stack grow into a resilient, lean, and future‑ready platform.
1. High availability and resilience
Modern users expect apps to load every time. Few moments sting harder than a service outage during peak traffic. A resilient design spreads risk and shrugs off surprises.
The Well-Architected Framework’s Reliability pillar urges you to distribute workloads across multiple Availability Zones so one local failure doesn’t topple everything.
Multi‑AZ and multi‑region patterns
Spreading workloads across at least two Availability Zones keeps power cuts or network blips from turning into headlines. Global brands often stretch further, pairing regions—say, us‑east‑1 with us‑west‑2—so natural disasters or large‑scale failures barely graze user experience.
For example, Route 53 health checks shift traffic away from trouble in seconds.
Automated failover with RDS and Elastic Load Balancing
RDS Multi‑AZ maintains a hot standby that stays in sync at the storage layer. When a primary node coughs, DNS flips automatically; no human fingers race across keyboards at 3 a.m. Elastic Load Balancers run continuous health probes and pull faulty instances out of rotation before customers hit a 500 error.
Proactive performance monitoring through Amazon CloudWatch
Composite alarms monitor key signals, such as latency, queue depth, and custom business metrics.
Early warnings let on‑call engineers intervene while the issue is still simmering, not a blaze. Over time, those alarms feed dashboards that spot trends long before they hurt revenue.
2. Cost optimization
AWS bills in fractions of a cent, yet those fractions add up fast. A runaway bill drains morale as quickly as cash. Cost‑aware design trims waste without slowing delivery.
Cloud spending grows quietly but bites hard. A cost‑aware game plan swaps waste for feature funding. Watch usage, right‑size gear, and lock in discounts once patterns settle.
Right‑sizing EC2 instances
Compute Optimizer will consume two weeks of CloudWatch data and then recommend smaller shapes or newer Graviton chips.
For instance, swapping an m5.4xlarge for an m6g.2xlarge often slices spend by a third and bumps performance per watt.
AWS trusted advisor cost checks
Weekly reports flag idle NAT Gateways, unattached EBS volumes, and forgotten load balancers. Clearing that clutter frees the budget for features users actually notice.
Savings plans and reserved instances
Predictable workloads lock in lower rates with one‑ or three‑year commitments. All‑upfront, partial, or no‑upfront options match nearly any cash‑flow plan.
Finance teams get predictable numbers, whereas engineers keep the freedom of on‑demand scaling.
3. Strengthening security posture
Security lapses can sink a business overnight, so the security pillar helps shield data, networks, and identities at every layer. Therefore, you’ll need a layered defense that shields data and keeps auditors calm.
Tight identity rules, nonstop scans, and strong encryption form the core.
AWS IAM least‑privilege access
Break sweeping roles into task‑based roles. The permission boundaries and service‑control policies block new projects from poking holes in production.
Continuous scans with Amazon Inspector
CVE checks run on EC2, Lambda, and container images. These findings flow into Security Hub, where severity filters push real fires to Slack or PagerDuty.
Encryption at rest & in transit (KMS, TLS)
Server‑side keys wrap S3, EBS, and RDS. Load balancers terminate TLS wherein the certificates are renewed through ACM. Data stays unreadable to prying eyes on every hop.
Raising operational efficiency
Engineers join to build, not just monitor servers. Code‑driven workflows, automatic patching, and smart alerts trade manual toil for focused progress.
Without standardized methods, daily cloud operations can become chaotic. The Operational Excellence pillar will tackle this challenge by promoting a mindset that favors automation, documentation, and iterative improvement.
Infrastructure as Code (CloudFormation, CDK)
Templates live in Git, turning environment builds into repeatable commands. Rollbacks mean git revert instead of late‑night console hunts.
Automated patching via AWS Systems Manager
Patch Manager groups fleets by tag, applies fixes during set windows, and shows compliance scores on a single dashboard. Logging & alerting with CloudTrail and GuardDuty
Every API call streams to S3, and GuardDuty crunches logs to flag odd behavior, like a new root key at 3 a.m. Alerts route to chat channels, where responders act fast.
4. Building for scalability
User growth rarely moves in neat lines. Elastic designs stretch and shrink on demand, sparing wallets and nerves alike.
The Performance Efficiency pillar demands AWS cloud architectures that expand or contract as load changes. Traditional monolithic setups might falter under sudden spikes, leading to slow response times or system crashes.
By contrast, an AWS-based microservices design can spin up new containers or functions as traffic rises, then reduce them when demand subsides.
Horizontal scaling with micro‑services
Break monoliths into small services behind Application Load Balancers.
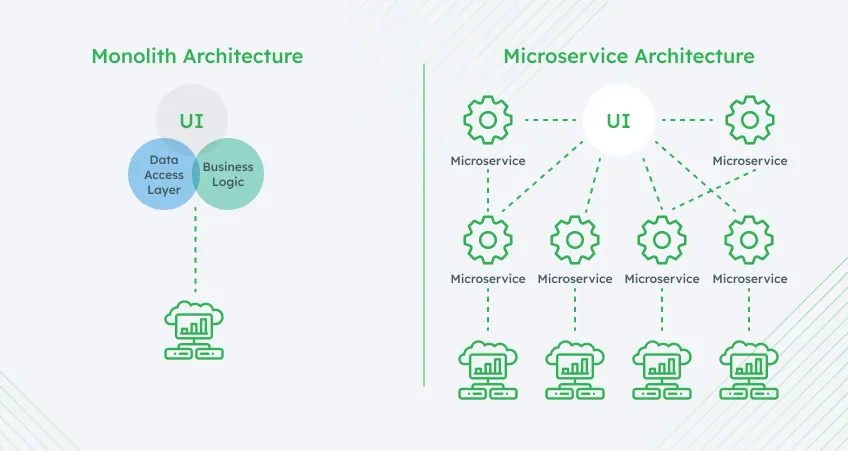
Auto-scaling groups add nodes when the CPU heats up and retire them during quiet hours.
Load testing for capacity planning
Distributed stress tests on Fargate or open‑source tools reveal the true ceiling before a marketing push. Decisions shift from guesswork to data.
Event‑driven design using Lambda & Amazon SNS
Functions react to events instead of polling. During flash sales, Lambda scales from zero to thousands of runs, then drops back to zero when the rush ends.
5. Cutting Environmental Impact (Sustainability)
Lower watt‑hours, lower bills, happier planet. Cloud choices can trim carbon without hurting performance.
The Sustainability pillar recognizes that workloads have an ecological footprint. Public cloud providers pool resources across many customers, which can boost hardware efficiency compared to on-premises data centers.
Choosing low‑carbon regions
Shift non‑latency‑sensitive workloads to eu‑north‑1 or ca‑central‑1, where renewable energy dominates. The Customer Carbon Footprint Tool shows grams of CO₂ saved each month.
Removing idle gear with usage reports
Cost Explorer’s low‑utilisation view spots instances loafing at five percent CPU and shutting them down trims carbon and spending in one click.
Preferring serverless or containers
Shared hardware multiplies utilization, where you’ll swap an always‑on batch server for a Step Functions‑plus‑Lambda flow can slash runtime hours by ninety percent.
6. Accelerating innovation
Fast feedback loops turn ideas into features users can touch. AWS Serverless scaffolds, automated pipelines, and instant test runs keep the momentum high.
Using the Well-Architected Framework encourages teams to adopt patterns that shorten feedback loops. For example, an application can be built on AWS Lambda, tested in a sandbox, and pushed to live users within days.
You can drive innovation in the following ways:
Building rapid prototypes on serverless & containers
Developers spin up APIs with AWS SAM or ECS Fargate in an afternoon, demo them the next morning, and refine them without begging for hardware.
Creating CI/CD pipelines via CodeBuild & CodePipeline
Commits trigger builds, unit tests, security scans, and blue‑green deploys automatically. Releases roll multiple times a day without weekend heroics.
Running automated tests for quick feedback
Lambda Power Tuner, CloudWatch Synthetics, and load‑test hooks run on every pull request. Bugs surface while the code is still fresh in the author’s mind.
7. Simplifying compliance and governance
Auditors want proof, not promises. Built‑in guardrails and live checks turn evidence gathering into a routine task instead of a drill exercise.
So, for industries facing anxiety over meeting HIPAA, PCI DSS, or similar standards, the Well-Architected Framework intersects with many of these mandates.
How?
For instance, encrypting data at rest with AWS KMS or enabling versioning in Amazon S3 helps address common rules found in healthcare or financial regulations.
Here’s further explanation on how you simplify compliance and governance.
Enabling policy guardrails with AWS organizations & service control policies
Global rules stop anyone from opening public S3 buckets or launching gear in unapproved Regions.
Real‑time checks through AWS Config rules
Rules fire when a resource drifts from baseline—think unencrypted EBS or missing tags. Alerts land in SNS topics, prompting instant fixes.
Centralised logging & auditing
CloudTrail streams to S3, Athena queries slice through months of data, and Lake Formation grants read‑only access to the audit crew. Evidence requests shrink from days to minutes.
Practical steps to integrate the AWS Well-Architected Framework
Rolling the Framework into daily life can be a challenging task to begin with. But consider it as a fitness plan for the cloud where you’d take honest measurements, target weak spots, and train in short bursts. An AWS Managed Service expert can act like a coach when progress stalls.
The cycle below turns that mindset into clear, repeatable moves.
Assess your system’s current state
A clear picture beats intuition.
So, start by turning every hunch about the stack into hard numbers and documented answers.
The following actions can help:
Run a thorough architecture review
Pull CloudWatch metrics and Trusted Advisor reports to back answers with numbers rather than hunches.
If the stack uses Lambda or IoT Core, attach the matching Lens to surface domain‑specific checks.
Here’s what it involves:
-
Well‑Architected Tool (WAT): Launch the questionnaire against one production workload. Scorecards flag red, yellow, and green areas across security, reliability, performance, and cost. Export the PDF so everyone agrees on the baseline.
-
Dig through CloudWatch: Build dashboards for latency, CPU, memory, queue depth, and any business KPI that matters. When a WAT question turns red, the matching metric usually tells you why.
-
Apply specialised Lenses: Serverless, IoT, or SaaS Lenses add domain‑specific checks. A Lambda‑heavy stack, for instance, raises questions on cold starts and concurrent limits that the core survey skips.
Identify Targeted Gaps
Raw findings need structure. Group issues by theme so the right squad tackles the right list, and nobody fights over priorities. Security gaps often show up first: wildcard IAM roles, open security groups, and unencrypted S3 buckets.
It's here, you take these steps:
Security & compliance
- Fire AWS Config rules that check IAM policies for wildcard actions, expired keys, and missing MFA.
- Scan VPC flow logs to spot unexpected outbound traffic—often a sign of flat network design.
- Tie each gap to a control requirement (HIPAA §164.308, PCI DSS 3.2.1 6.4.1, and so on) so auditors see instant alignment.
Cost & performance
- Overlay Trusted Advisor’s idle‑resource alerts with CloudWatch utilisation graphs. A t3.medium cruising at five‑percent CPU sticks out in seconds.
- Review storage classes: warm data sitting on GP3 or Provisioned IOPS volumes quietly drains dollars.
- Flag chatty micro‑services that cross AZ boundaries too often; cross‑zone traffic fees add up fast.
Reliability & operational quality
- Inspect AWS Backup plans—daily snapshots mean little if the restore test fails.
- Time a full restore into a sandbox account, then compare the clock against stated RTO goals.
- Open runbooks and look at the last edit date; stale docs usually signal outdated procedures.
Plan iterative improvements
Smaller sprints keep morale high and wins visible—rank risks by blast radius and ease of repair. Within the first sprint, tackle high‑impact, low‑effort items, like turning on S3 versioning.
Create a prioritized roadmap
- Rank gaps by blast radius and fix effort. Public S3 buckets top the list, slow queries land later.
- Bundle tasks into two‑week chunks so teams deliver visible progress every sprint.
Read more: Complete guide to using AWS CDK for IaC Development
Automate deployments & testing
- Store every stack in CloudFormation or the CDK. Merge requests trigger CodePipeline, which runs cfn‑nag, unit tests, and security scans before deploying.
- Add load‑test hooks—think distributed artillery scripts on Fargate—to validate performance with each change.
Set measurable KPIs
- Aim for numbers like “cut EC2 spend by 25 percent” or “halve p95 latency.”
- Expose those metrics on a public (inside the company) dashboard; green bars build confidence, red bars prompt fast action.
Utilize AWS partners or consultants
Fresh eyes and proven playbooks shave months off the journey.
Pick numbers that matter. For example, reducing monthly EC2 spending by 25 percent, cutting mean time to recover (MTTR) to under ten minutes, or dropping p95 latency below 300 ms.
Well‑Architected partner program
- Certified AWS cloud consulting partners run funded reviews, and AWS often hands out service credits when high‑risk items drop below the threshold.
- Partners bring reusable Terraform or CDK modules that shortcut common fixes.
Dedicated support & rolling audits
- Schedule quarterly WAT re‑runs to catch drift early.
- Managed services teams handle patch cycles, backup verification, and compliance scans, freeing in‑house engineers for new features.
Mentorship & knowledge transfer
- Hands-on workshops cover IaC patterns, cost drills, and incident response simulations.
- Recorded sessions and template libraries remain long after the consultants step away, keeping internal skills sharp.
Conclusion
The AWS Well-Architected Framework answers a common question: “How do we run secure, scalable, and cost-conscious cloud workloads?”
By centering on six clear pillars, teams can pinpoint areas that need fixing and steadily adopt changes that drive real outcomes—fewer outages, stronger defenses, and smarter spending.
If you’re exploring ways to strengthen your AWS setup, Peerbits can be your partner. We’ll coordinate a detailed review, recommend concrete steps, and ensure your staff gains the skills to keep everything on track.