In today’s rapidly evolving world of digital transformation, IoT seamlessly integrates with industrial processes to create smart factories. These advanced environments leverage automation to enhance productivity and operational efficiency. Driving this transformation are Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solutions, which revolutionize data sharing and empower data-driven decision-making to optimize production.
Manufacturing businesses are adopting Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) to improve their performance and make the most out of their existing resources.
The worldwide market of IoT in the manufacturing market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1%, from $33.2 billion in 2020 to $53.8 billion in 2025.
Industries can link and automatically integrate items and processes to construct cyber-physical systems, which form the base for Industry 4.0. The prime objective of Industry 4.0 is to deploy newer technologies to create value in manufacturing businesses while reducing waste.
Businesses can adopt IoT in industrial automation to optimize workforce efficiency and achieve a higher return on investment. IoT applications in manufacturing are a key driver of Industry 4.0. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of IoT manufacturing, covering trends, IIoT insights, implementation strategies, impacts, applications, benefits, and challenges.
IoT trends in manufacturing for 2025
In 2025, the application of IoT in manufacturing will focus on AI-driven analytics for deeper insights and smarter decision-making. The rise of 5G connectivity promises faster and more reliable communication between IoT devices, enhancing operational efficiency.
Sustainability will also play a key role, with IoT systems being used to monitor and reduce energy usage. Advancements in edge computing will enable real-time data processing at the device level, further boosting the potential of IoT in the manufacturing industry. Businesses looking to stay ahead should closely monitor these trends.
What is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
In simple terms, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the application of IoT technologies in industrial and manufacturing settings. It connects industrial assets such as machines, equipment, trucks, warehouses, shop floors, and inventories through the Internet where they can collect, exchange, and analyze data in real-time.
The digital transformation in manufacturing creates smart, automated environments that enhance productivity, efficiency, and decision-making. Let’s look at its components to understand the core functionality of IIoT in detail.
Components of IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things)
IoT applications in manufacturing need to blend with the day-to-day objects that are useful for manufacturing businesses. To better understand the functioning of Industrial IoT systems, here’s a detailed look at the components of IIoT that remain at the core of this robust, modern technology:

1. Smart assets
Smart assets in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are physical devices, equipment, or systems that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity features that help in collecting, processing, and exchanging data in real-time.
These assets are "smart" because they can monitor their status, communicate insights, and often take autonomous actions based on their operational conditions which leads to delivering smart inventory management solutions through the value chain of information.
Examples of intelligent assets of IIoT are;
- Plants instrumentation
- Digital equipment
- Embedded systems
- Edge devices
2. Software and analytics
IIoT relies on the software to process the data that devices and systems collect at various touchpoints. It also offers an interface through which you may communicate with other systems.
IoT in manufacturing can help businesses profit from cloud-based software over on-premise software. This increases the speed, flexibility, and dependability of the system.
3. Data communication infrastructure
Other technologies and the internet are necessary for the IIoT system's cte. IIoT solutions are increasingly implemented on cloud infrastructures such as Amazon Web Services to store remote servers, and manage, and process data in these systems.
4. Existing enterprise application
It is impossible to successfully install an IoT business solution unless it works smoothly in tandem with essential corporate apps to enhance fundamental business operations.
Here, enterprise inventory management can get data inputs from business applications like ERP, CRM, BMS, MES, SaaS, and mobile applications that are used to monitor and control instrumented assets.
You also have legacy applications like mainframe or operational technologies that need to be part of the package with new IoT-based asset management solutions to get the most benefit using enterprise applications.
5. Manpower
This is a crucial and perhaps the most underappreciated aspect of IIoT. People engage with the system by making data and analysis-driven decisions. The higher the data quality, the better the findings will be.
As a result, the interaction between humans and other IoT components like fleet and asset tracking solutions maintains a measured balance.

Implementing IoT in manufacturing
Implementing IoT in manufacturing bridges the gap between understanding its components and putting them into action. With a clear grasp of IIoT fundamentals, manufacturers can now focus on creating smarter, more efficient workflows that deliver tangible benefits.
- Assess current systems: Evaluate existing equipment and identify areas where IoT can add value, such as predictive maintenance or real-time monitoring.
- Define clear objectives: Establish specific goals, such as reducing downtime, improving production efficiency, or improving product quality.
- Choose the right IoT platform: Select a scalable and secure platform that lines up with your business goals and integrates with existing systems.
- Invest in secure connectivity: Deploy reliable network solutions, like 5G or Wi-Fi 6, to ensure smooth communication between devices.
- Build a skilled team: Train personnel to manage IoT devices, analyze data insights, and optimize operations.
- Pilot and scale: Start with a small-scale implementation to test feasibility, then gradually expand to full-scale operations. Implementing these steps allows manufacturers to move from theory to practice, covering the way for efficient and innovative IoT-powered operations.
Impact of Industrial IoT on core manufacturing areas
By injecting innovation into old processes, the Internet of Things is transforming four essential manufacturing areas. Let us understand each in a brief way to optimize these touchpoints to improve operational efficiency through industrial IoT solutions.
1. Shop floor operations
Real-time data on operations and the state of spare parts are gathered by sensors installed in machinery. After that, the information will go to a cloud platform for analysis.
The findings will be on the screen of the user's application, giving shop floor supervisors a complete picture of the manufacturing process.
It is now possible to continually monitor production conditions and make data-driven choices in real-time to keep equipment in good operating order and enhance product quality.
Wearable IoT in manufacturing can help track the health and whereabouts of industrial personnel working in hazardous areas, hence improving their safety.
2. Remote and 3rd party operations
New-age businesses will not be bound to a single location; instead, they often have a network of associate firms and branches spread throughout cities, regions, and nations.
They can also outsource manufacturing activities to third-party firms to save shipping and infrastructure expenses.
All remote and outsourced operations may be monitored using IoT and smart manufacturing and services as a single process. This is the most effective technique that ensures all contractors follow the technological revolution and that the finished items meet established requirements.
3. Supply chain
End-to-end manufacturing supply chain management is possible by implementing IoT sensors and warehouse management software.
Manufacturers may track the movement of vehicles transporting supplies and commodities, view extensive information on things in warehouses, and regulate the conditions (temperature, humidity) in which products are stored or moved.
Managers intending to build and promote flawless operations in their businesses can greatly benefit from supply chain management solutions enabled by effective transparency.
4. Workshop mirroring
The Internet of Things may connect Market-Ready Solutions (MRS) with business information management systems. It assists businesses in automating the control of IoT-enabled industrial processes carried out in workshops. Industrial IoT solutions help access, identify, and control the manufacturing execution process.
Modern businesses foraying into Industry 4.0 in supply chain management can use IoT to monitor all situations from the commencement of manufacturing to the final delivery of the product.
An industry's production and product-related input data passes from multiple IoT-enabled manufacturing layers. IoT and smart manufacturing with modern devices allow businesses to solve connectivity, computing, and control concerns properly.
Read more: IoT in manufacturing: Predictive maintenance & quality control
Application of IoT in manufacturing
In manufacturing, the Internet of Things provides a win-win situation for manufacturers and consumers. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) allows manufacturers to scale up various equipment that can be remotely monitored and repaired. As a result, businesses can accurately predict their consumers' demands.
As a manufacturing industry, the Internet of Things can revolutionize business. Networked control systems already aid process and monitoring in several facilities to apply this modern technology at various levels. Let us check them out!
1. Smart packaging
For producers, smart packaging directly employs materials with interconnected embedded systems to offer IoT benefits. The most crucial feature of smart packaging is that it allows customers to interact with it while also generating data that can be useful to manage a product better.
For instance, smart packaging includes culinary videos, beauty tips, and other demos to illustrate using the product.
Sensors, QR codes, AR, VR, and mixed reality possibilities are some of the ways IoT and packaging interact together. The goal is to provide customer value while simultaneously collecting data using smart asset tracking solutions that improve operations and efficiency.
2. Remote production control
Remote process monitoring and equipment configuration are possible with IoT in manufacturing. For starters, personnel may collect data on manufacturing processes from afar and determine if their consequences comply with certain rules and standards.
Second, they can remotely tweak and set up equipment, saving them a lot of time and work.
Furthermore, businesses can opt for IoT software development services to resolve numerous performance concerns via virtual networks without being physically present, simplifying equipment administration and control. Employees can also be aware of the position of devices, such as moveable assets, using virtual equipment monitoring.
3. Predictive maintenance
Human participation is no longer necessary to predict abnormalities in equipment performance: embedded IoT sensors in machines can detect any operational malfunction like temperature, pressure, voltage, etc. and alert responsible personnel, leaving employees to only take remedial action.
Predictive maintenance, also known as predictive mending, allows technical support personnel to discover and address faults before they lead to major equipment failure, minimizing downtime and expenses.
Predictive maintenance also allows IoT-connected equipment to be integrated with advanced analytics tools to predict when technical help is required.
4. Asset management
Manufacturers may acquire and monitor real-time information on all of their assets through the web or mobile applications. Industrial asset tracking with IIoT devices ranging from the supply chain, vehicle transporting raw materials and goods, Warehouse items, and production process-related resources to the finished product.
Asset monitoring allows for the early and accurate detection of faults that negatively influence product quality or time-to-market.
5. Digital twins
The Internet of Things, AI, machine learning, and cloud computing are all digital twin technologies. The digital transformation in manufacturing is enabled by digital twins that work as virtual replicas of actual products, and their use on the factory floor may be extremely beneficial.
Engineers and managers may mimic various processes, run tests, find faults, and achieve desired results using virtual duplicates of equipment and replacement parts without jeopardizing or harming actual assets.
Benefits of IoT in manufacturing
In terms of operations and procedures, this network gives insight into what is working and what isn't. Your company's ERP system is the most likely system to assist you in interpreting the data you've collected.
We can now check out a few of the top advantages of industry 4.0 applications in manufacturing for time to come.
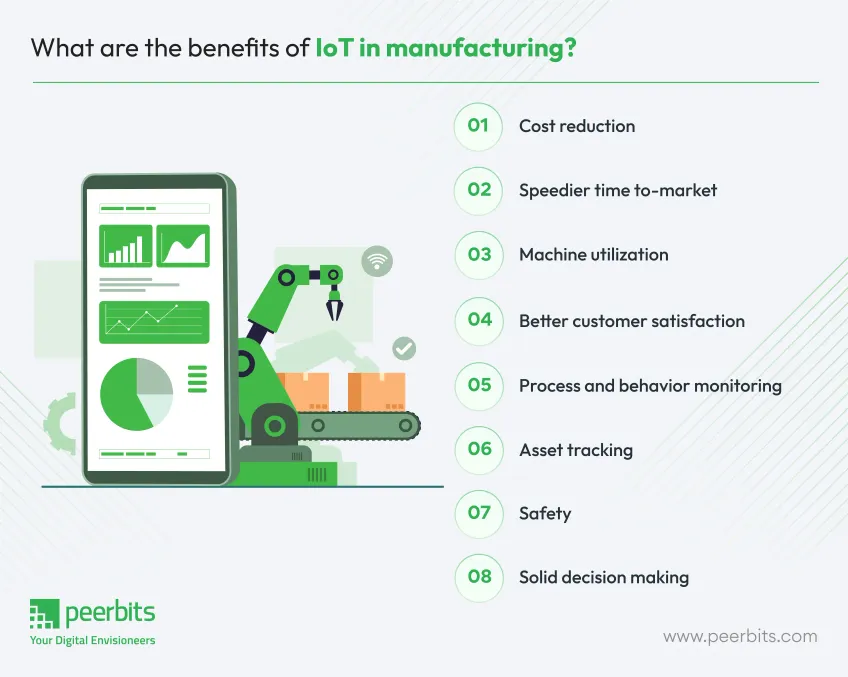
1. Cost reduction
Energy, materials, and downtime losses are high costs for manufacturing companies. Process automation is a trademark of the Internet of Things, and it results in a considerable decrease in operating expenses.
When combined with better asset management, predictive maintenance prevents a lot of potential problems and saves money.
2. Solid decision making
Comprehensive data is necessary for resource management and asset optimization that involves both humans and machines. IoT-based sensors collect vital data and deliver it in real time across resilient networks.
Fast data flow throughout the production plant allows for the continuous generation of dashboard metrics that aid in disseminating findings and decision-making.
Managers have precise insights and are always aware of their systems and devices' functioning thanks to IoT development in manufacturing, resulting in speedier and better-informed decision-making.
3. Speedier time-to-market
IoT allows for direct connection between employees and network components, dramatically boosting productivity. Real-time data availability also allows for quicker decision-making and better responsiveness to market volatility.
As a result, new goods move fast from concept to market, resulting in considerable time savings.
4. Safety
In many industries and factories, IoT sensors monitor working conditions. For example, the number of dangerous pollutants and wearable devices that monitor workers' health assist in creating a safer working environment and preventing numerous accidents.
5. Better customer satisfaction
Quality is the make-or-break element in how potential consumers behave and whether or not they become loyal customers. Predictive maintenance tools and statistical assessments are provided by the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technology.
This will help innovation, planning, design, construction, operation, and maintenance of industrial facilities, resulting in higher product quality.
6. Asset tracking
Fleet and asset-tracking solutions keep businesses informed by monitoring items throughout the supply chain. They provide real-time updates and notify stakeholders about delays or issues.
7. Machine utilization
The IIoT lets machines be connected to the internet, providing you access to machine lifelines and KPIs. This information is useful in identifying the reasons for unscheduled downtime.
8. Process and behavior monitoring
Managers in business organizations and companies may use IoT data to obtain insight into their workers' performance. For example, a root cause analysis might unravel that workers routinely create defections due to this process. This equates to increased scalability, cost savings, and quality assurance.
Challenges in the adoption of IoT in manufacturing
Despite its potential, adopting IoT in manufacturing comes with hurdles. Two main challenges in adopting IoT in manufacturing include:
- One major issue is data security, as IoT devices can become vulnerable to cyber threats without proper measures.
- High initial investment costs often deter smaller businesses from embracing the Internet of Things in manufacturing.
- Another challenge lies in the lack of skilled personnel to manage and optimize IoT systems.
- Compatibility issues between legacy equipment and modern IoT solutions can also slow progress.
- Addressing these challenges can help businesses achieve smoother adoption.
Conclusion
Businesses can adopt industrial IoT systems that help maximize productivity by ensuring production uptime, lowering expenses, and eliminating waste.
Manufacturers may better know their production and supply chain operations, increase demand forecasting, reduce time to market, and improve customer experience by utilizing IoT data.
However, given the scope and complexity of Industrial IoT efforts, effective IIoT adoption necessitates careful orchestration across all IIoT application design and execution segments.

FAQ
Common challenges include ensuring data security, integrating IoT with legacy systems, addressing high implementation costs, and bridging the skill gap in handling IoT technologies.
IoT-enabled devices analyze production lines in real time, detecting defects early. This helps maintain product consistency and reduces material wastage, leading to cost-effective quality control.
IoT solutions automate routine tasks, optimize resource usage, and improve decision-making through data-driven insights letting SMEs compete with larger manufacturers.
Emerging trends include the adoption of 5G networks for faster connectivity, edge computing for quicker decision-making, AI-driven analytics for smarter operations, and green IoT solutions promoting sustainability.
IoT connects smoothly with existing ERP and MES systems through APIs and IoT gateways. This ensures efficient data sharing and better operational coordination.
IoT monitors resource consumption, reduces waste, and optimizes energy usage. These IoT applications help manufacturers meet environmental targets while maintaining profitability.








